ALHAMBRA Gold catalog
The ALHAMBRA-survey
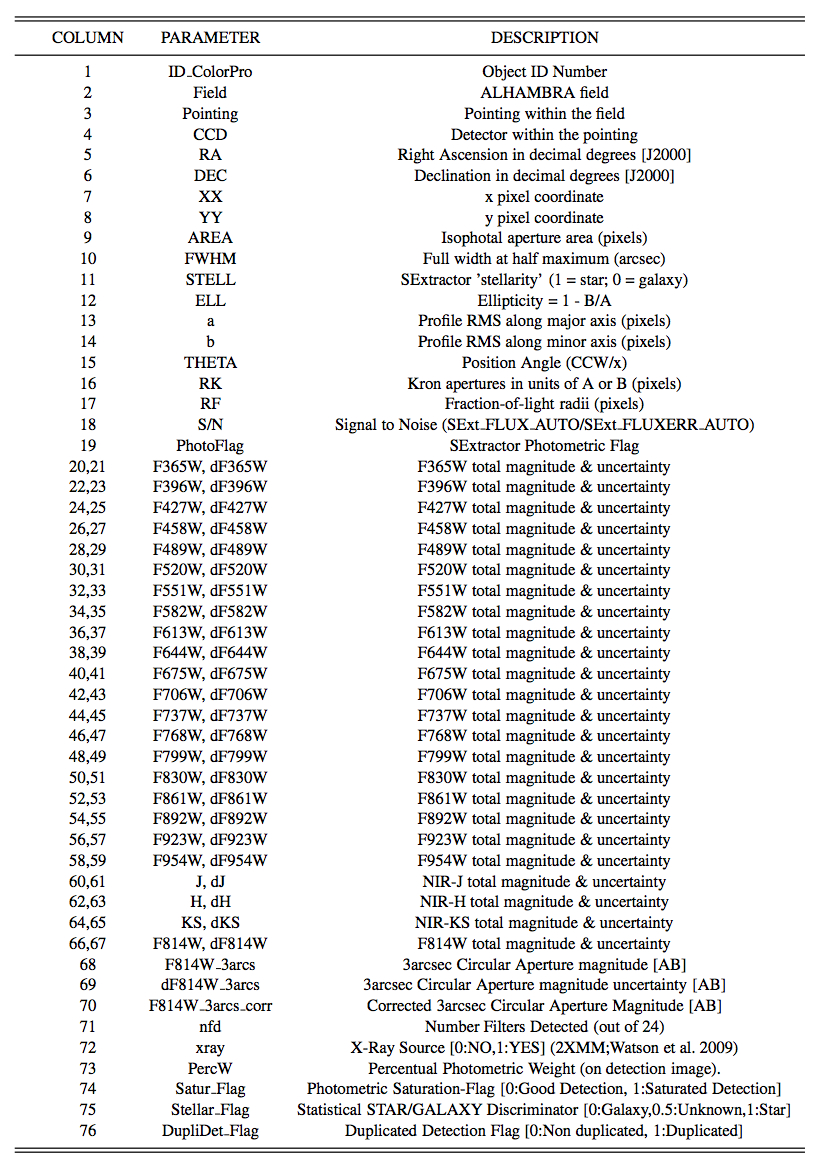
The ALHAMBRA (Advance Large Homogeneous Area Medium Band Redshift Astronomical) survey (Moles et al. 2008) has observed 8 different regions of the sky, including sections of the COSMOS, DEEP2, ELAIS, GOODS-N, SDSS and Groth fields using a new photometric system with 20 contiguous, non-overlapping, equal width (∼300Å) filters, covering the optical range (3500Å-9700Å), plus the standard broadband NIR J, H & Ks filters. The observations were carried out with the Calar Alto (CAHA) 3.5m telescope using the wide field, 0.25 deg2 FOV optical camera LAICA and the NIR instrument Omega-2000. The ALHAMBRA survey dataset represents a ~700hrs of total exposure time, gathered in between the 2005 and 2012.
The ALHAMBRA photometric system was specially designed to maximize the effective depth of the survey, in terms of accurate spectral-type and photometric redshift estimations, along with the capability of identification of relatively faint emission lines (Benítez et al. 2009).
The ALHAMBRA Gold Catalogue
The ALHAMBRA Gold Catalogue (Molino et al. 2013) corresponds to a subsample of ~100k galaxies, photometrically complete down to a magnitud I=23 AB, covering a total area of 3 deg2, spread over 7 non-contiguous regions of the sky, with an on-target exposure time of ~32hrs.
The catalogue provides PSF-corrected photometry for 20+4 bands and accurate photometric redshift estimations, with an expected error dz/1+z<0.012 and redshift probability distribution functions P(z) well described by a single Gaussian peak. (Molino et al. 2013, Section 4.1).
The catalogue also includes photometric information for ~20.000 stars in the galactic halo, identified according to their apparent geometry, F814W magnitude, optical F489W-F814W & NIR J-Ks colors, as explained in Molino et al. 2013, (Section 3.6).
In addition, the catalogue includes ~1.000 AGN candidates identified according to a new methodology described in Molino et al. 2013 (Section 4.6).
Catalogues & Images notation
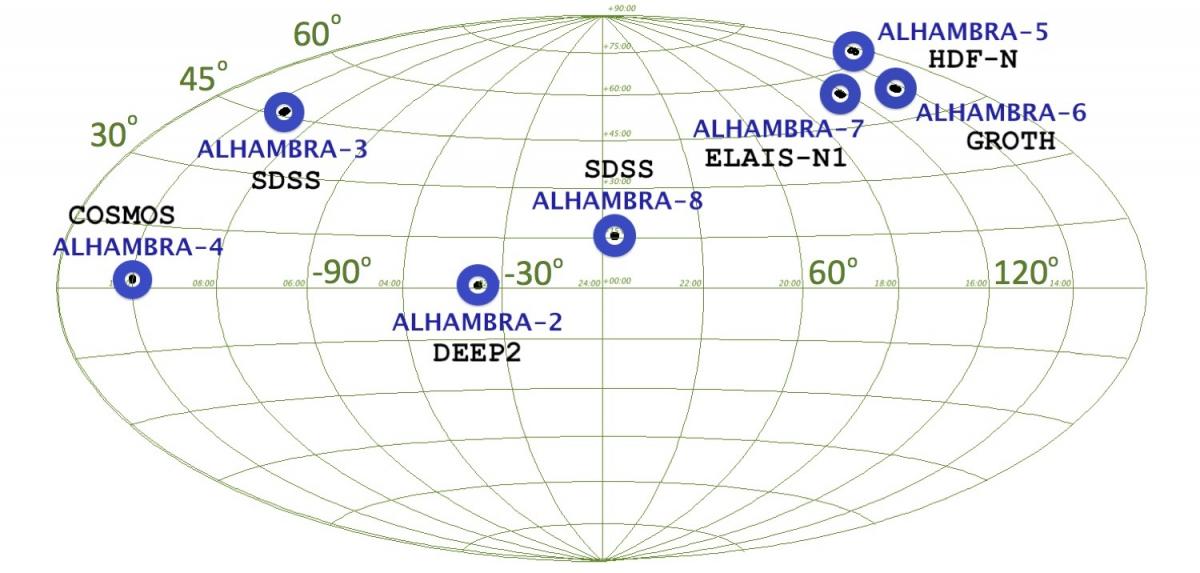
The figure above illustrates an example of the Pointing Layout for the ALHAMBRA fields. Given the geometrical configuration of the optical imager LAICA, each pointing is composed by four CCDs (as marked with the yellow squares) with an internal gap of ~13.0'. The combination of two contiguous pointing yields a final layout composed by two strips of 58.5'x15.5' (comprising four individual CCDs each). Contiguos CCDs within each strip show a maximum overlap of 4.0'x15.5'.
Therefore, the catalogue notation is tied to the corresponding detection image F814W, which cames defines by the position it takes within the ALHAMBRA fields.
Example:
The detection image alhambra.gold.F02P01C02.F814W.fits, corresponding to the Field:2 (F02), Pointing:1(P01) and CCD:2 (C02), may have an associated catalogue: alhambra.gold.F02P01C02.ColorProBPZ.cat
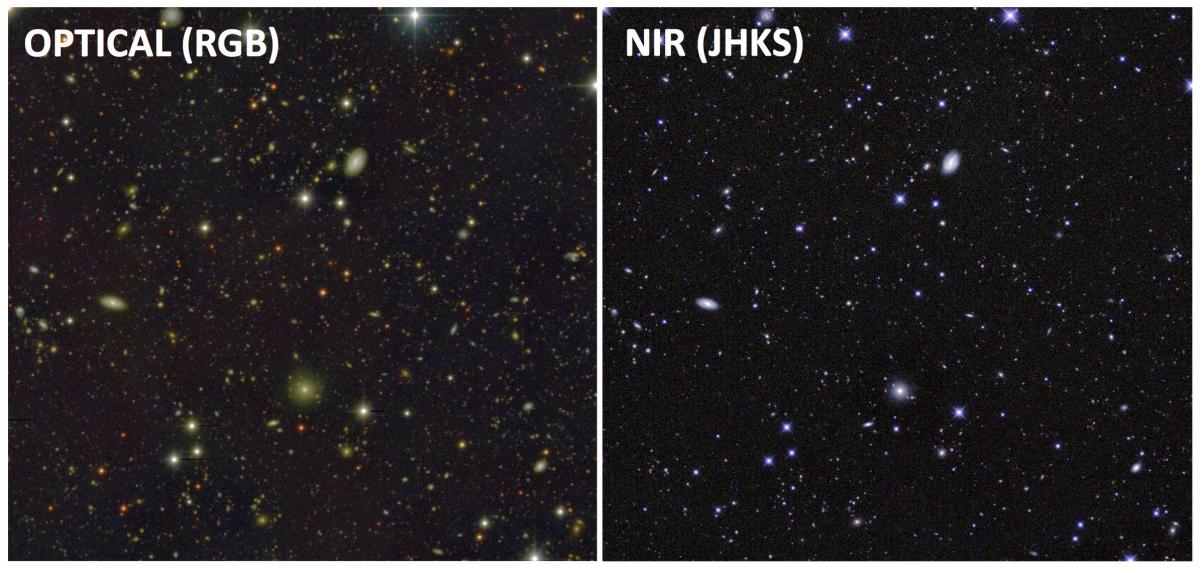
In addition, color images related to the former detection image F814W may have the following notation:
alhambra.gold.F02P01C02.OPT.png for the optical range (RGB)
alhambra.gold.F02P01C02.NIR.png for the NIR range (JHKS)

Catalogue description
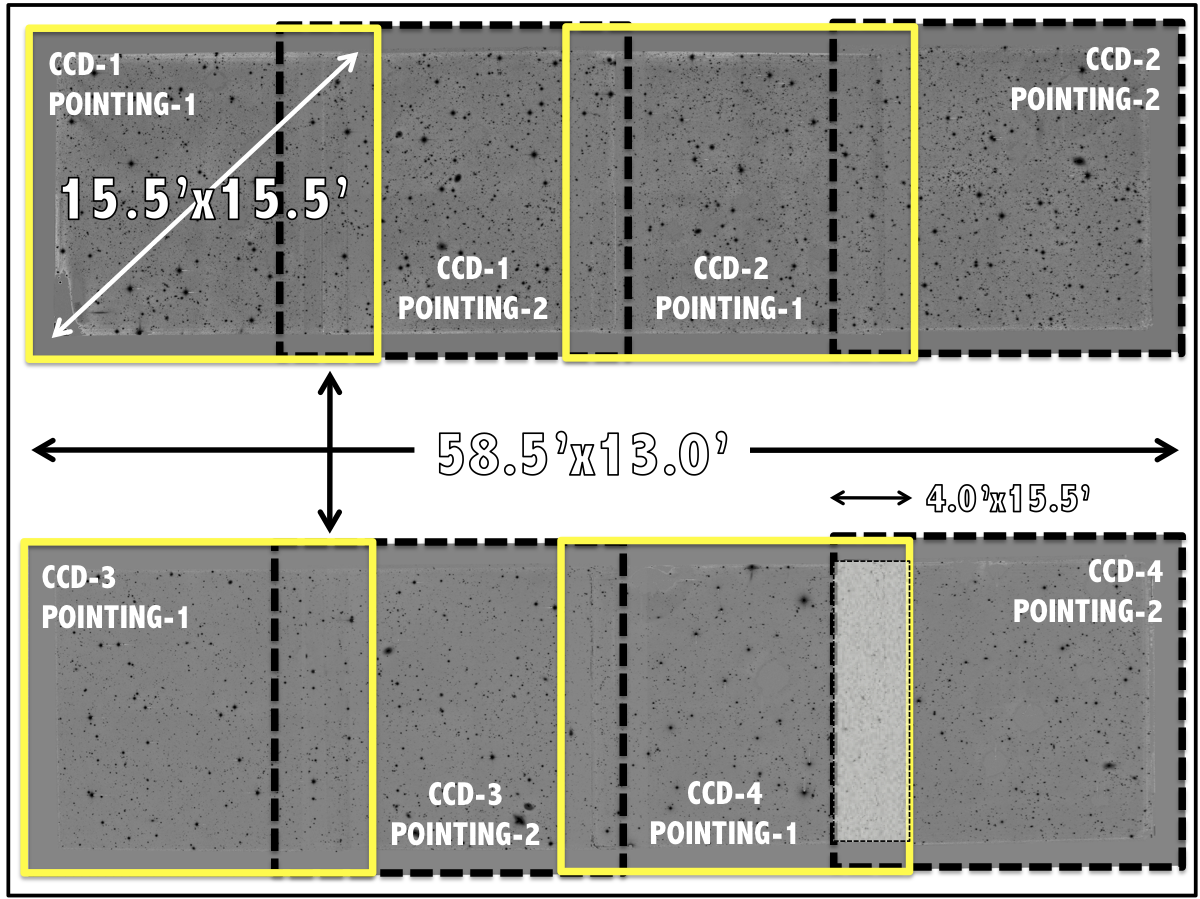
Unique IDs are given to every detection according to the following criteria: ID = 81442100119 stands for 814 (detection image) + 4 (Field) + 2 (Pointing) + 1 (CCD) + 00119 (ColorPro ID). Both astrometric and geometrical information is derived from its corresponding F814W detection image. Kron apertures (RK) and fraction-of-light radii (RF) were settled according to the aperture parameters defined in Molino et al. 2013 (Table D1). Total magnitudes and empirically corrected uncertainties (Molino et al. 2013, Section 3.7) are given by all the 24 filters. Along with this, F814W_3arc represent F814W magnitudes measured on a 3” circular apertures and ditto F814W_3arc_corr but corrected to tied COSMOS/F814W photometry (Molino et al. 2013, Section 3.5). As every detection in the ALHAMBRA fields was covered by all the 24 filters, nfd indicates the number of filters a source was detected. Whenever a source was not detected, its magnitude was set to 99. and its photometric uncertainty replaced by a 1-σ upper limit (Molino et al. 2013, Section 6.1) suitable for BPZ.
Final catalogues contain several quality flag. PhotoFlag corresponds to the standard SExtractor photometric flag (Bertin & Arnouts 1996), Satur_Flag indicates a possible saturated source (typically stars with magnitudes brighter than F814W=16), Stellar_Flag represents a source-by-source statistical classification among stars and galaxies (Molino et al. 2013, Section 3.6), irms_OPT_Flag and irms_NIR_Flag indicates the number of optical and NIR bands a detection was observed with a normalized exposure time below its 80%, respectively. The DupliDet_Flag indicates either a source was detected twice (within the overlapping area among consecutive detectors). If so, the detection with the poorest S/N is set to a value DupliDet_Flag=1. Therefore, selecting detections with DupliDet_Flag=0 removes all duplicated detections when combining catalogues.
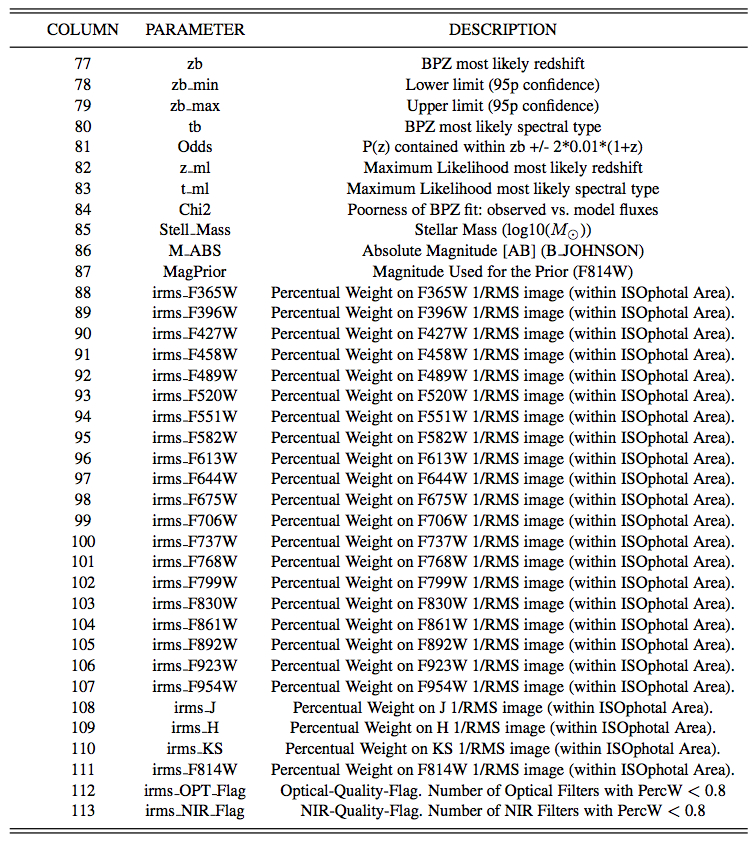
The most likely photometric redshift solution for every source is assigned by zb_1. Additionally, zb_min_1 and zb_max_1 represent the lower and upper limits for the first peak within a 95% interval. Spectral-type classification is given by tb_1 where its number refers to the selected template, as indicated in Molino et al. 2013 (Fig. 21). Odds_1 gives the amount of redshift probability enclosed around the main peak (Molino et al. 2013, Section 4) and χ2 the reduced chi-squared from the comparison between observed and predicted fluxes according to the selected template and redshift. An estimation of each detection stellar mass content (in units of log10(M⊙)) is given by Stell_Mass_1. M_ABS_1 corresponds to the absolute (AB) magnitude for the Johnson B-band. MagPrior corresponds to the F814W magnitude used to derived the BPZ Prior. Finally z_ml and t_ml represent again the most likely photometric redshift and its spectral-type but estimated using a maximum likelihood (instead a Bayesian approach).
The following tables summarize the complete catalogue containt.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
Each catalogue contains useful information stored on its header, regarding observational conditions and photometric zeropoint corrections (ZPC) derived using BPZ (Molino et al. 2013, Section 4.2).
As magnitudes have been corrected (applying the so-derived ZPC) to fit the galaxy colors, magnitudes for all non extragalactic sources (as stars) might be restored by subtracting those quantities (ZPC).
An example of the information stored on the catalogues header:
############################################################################################
## This proprietary file was created by the ALHAMBRA-survey: Moles, M., et al. 2008, AJ, 136, 1325
## ALHAMBRA-survey Field: F02P01C03
## Release Date (v1.0): 2013-June-21
## Field Target Point: R.A. = 37.0153, Dec. = 0.6626 (J2000)
## Reddening [E(B-V) = 0.031] (Schlegel et al. 1998)
## Area: 15'x15'
## Telescope: 3.5m on Calar Alto (www.caha.es)
## Epoch Observation Dates: 2005-2012
## Based on images produced by the ALHAMBRA-survey: Cristobal-Hornillos et al.2009, ApJ, 696,1554
## Photometric ZP based on Spectro-photometric stars: Cristobal-Hornillos et al.2013 (in prep.)
## PSF-corrected Photometry using ColorPro software: Coe et al. 2006
## Detection-Image: Synthetic F814W HST/ACS
## Kept detections with S/N > 3 (on detection image)
## mag, magerr = 99, 1-sigma limit: non-detection (flux < 0)
## Photometric Redshifts performed using PSF-corrected photometry + BPZ: Molino et al. 2013
## ZP-corrections derived with BPZ ALREADY applied to the current photometry.
## Any further information, please contact with:
## Alberto Molino: amb@iaa.es
## Txitxo Benítez: benitez@iaa.es
############################################################################################
## FILTER ZP ZPCorr GalExt mlim (3",5-sig) FWHM ["]
## F365W 31.091 -0.105 0.155 23.28 1.33
## F396W 31.134 0.092 0.146 24.18 1.17
## F427W 31.279 0.031 0.136 25.56 1.02
## F458W 31.686 -0.086 0.127 23.37 1.12
## F489W 31.698 0.098 0.118 24.76 1.06
## F520W 31.550 0.099 0.110 26.34 0.92
## F551W 31.552 0.062 0.101 25.48 0.99
## F582W 31.606 0.124 0.095 23.75 1.05
## F613W 31.453 0.149 0.088 24.43 1.06
## F644W 31.597 0.103 0.084 24.26 1.22
## F675W 31.573 0.073 0.079 23.64 1.08
## F706W 31.351 0.082 0.076 23.94 1.20
## F737W 31.233 0.085 0.071 23.64 1.50
## F768W 30.998 0.127 0.065 24.79 1.01
## F799W 30.809 0.080 0.062 23.41 1.47
## F830W 30.558 0.073 0.057 24.44 1.02
## F861W 30.733 0.128 0.053 24.85 0.94
## F892W 30.085 0.106 0.050 24.82 0.73
## F923W 29.760 -0.009 0.046 23.71 0.93
## F954W 28.870 0.214 0.043 19.79 1.49
## J 29.154 -0.001 0.029 22.90 1.07
## H 29.359 -0.109 0.017 22.61 1.00
## KS 28.560 -0.051 0.011 24.88 0.97
## F814W 30.640 0.000 0.060 22.62 1.06
## F814W_3arcs 30.640 0.000 0.06 22.62 1.06
## F814W_3arcs_corr 30.640 0.000 0.060 22.62 1.06
############################################################################################
Download catalogues and images:
Catalogues and detection images can be freely accessed here:
or using the Spanish Virtual Observatory here
Download the Molino et al. 2014 paper in High Resolution:
The "The ALHAMBRA-survey: Bayesian Photometric Redshifts with 23 bands for 3 squared degrees"
paper (Molino et al. 2014) can be reached here.
Further information:
If you have questions or need any further information, you can reach us:
by email: Alberto Molino ( amb@iaa.es ) // Txitxo Benítez ( benitez@iaa.es )
by phone: (+34) 958.230.626